Here’s a brief article on the 1963 Czechoslovak Championships, which Šťastný and Čáslavská won. Čáslavská swept the event titles, as well.
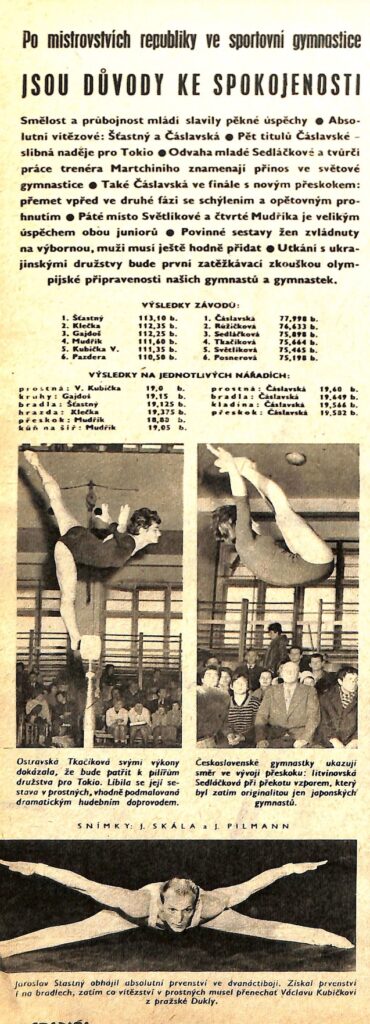
twentytwenty domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /www/gymnasticshistorycom_663/public/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121Here’s a brief article on the 1963 Czechoslovak Championships, which Šťastný and Čáslavská won. Čáslavská swept the event titles, as well.

The Czechoslovak men’s team used to be the strongest program in the world. The Czech Sokols won the team titles at the 1907, 1911, 1913, 1922, 1926, 1930, and 1938 World Championships. After World War II, Czechoslovakia’s highest finish at the World Championships was third (1958 and 1962).
So, what happened? Why was their program struggling? In 1963, Stadión ran an article that offered several theories on this topic. The main concern was a lack of depth.
This lack of depth was, in part, due to the amount of dedication that gymnastics takes. “Gymnastics needs all of one’s free time. And so the boys leave and are content to perform some kind of handstand or somersault in the swimming pool.”
Another reason was Czechoslovakia’s mandatory military service, which happened at an age when male gymnasts are just starting to gain the strength required for high-level gymnastics. One unit — Dukla in Prague — was good at developing gymnasts while those who go to other military units do not progress. As a result, many male gymnasts’ development fell by the wayside at the age of 19.
In addition to the question of depth, there was a lack of consistency in the training methodologies throughout the various regions. And generally speaking, there seemed to be misguided routine composition among the top Czechoslovak men.

In 1963, Japanese gymnasts traveled to Czechoslovakia for a dual meet. Not surprisingly, the Soviets, specifically Yuri Titov, made a trip to Czechoslovakia to film the routines, and the East Germans were there with their notepads.
According to an article in the Czechoslovak sports magazine Stadión, the Japanese men’s artistic gymnasts were breaking new ground on rings and high bar, while the Czechoslovak women’s artistic gymnasts were showing original elements on beam and floor. (Though, the Japanese women’s artistic gymnasts were the queens of turns on beam.)
Here’s a short account of what happened.
Reminder: This was a competition between the top teams in the world. The Czechoslovak men’s team finished third at the 1962 World Championships while the Japanese men finished first. The Czechoslovak women’s team finished second in 1962 while the Japanese women finished third.
When Čáslavská won the vault title at the 1962 World Championships, Vladimír Prorok was her coach. He was the 1955 European Champion on floor exercise, and when he was coaching Čáslavská in the early 1960s, he was a relatively new but highly dedicated coach — one whom “foreign countries look up to with envy and speak of with the utmost respect.”
Note: Prorok also means “prophet” in Czech. Hence the prophecy references throughout this piece.

Luděk Martschini was a coach in the small town of Litvínov, Czechoslovakia. One of his most notable gymnast was Jaroslava Sedláčková, who was part of the 1964 Czechoslovak team that won silver and the 1966 team that won gold. Martschini would go on to be the head coach of the Swiss women’s team during their Olympic debut in 1972.
A 1963 profile of Martschini portrayed him as a man who was devoted to his work (perhaps overly devoted?) and whose anger flared up when a gymnast did not do her homework. The denizens of the town were reluctant to embrace gymnastics, especially leotards, but once his gymnasts started winning, the town embraced gymnastics enthusiastically, and his group of trainees began to grow.
The profile touches upon well-worn topics in gymnastics coverage. For example, can a gymnast have all three — gymnastics training, a good education, and a boyfriend? “School, boyfriend, and sports are an unforgiving triangle. So far, gymnastics wins for everyone, even though school is of course a given.”

At the 1962 World Championships, Přemysl Krbec of Czechoslovakia won the gold medal on vault. This was the last time that a Czechoslovak gymnast was a world champion in men’s artistic gymnastics. Since there hasn’t been much written about Krbec, I translated a profile that was published after the 1962 World Championships in Prague.
Like many gymnasts, gymnastics was not his first love. Even though both his parents were gymnasts, he loved soccer.
Heads-up: Holub, the author of this profile, tended to be a bit fanciful in his profiles of gymnasts.

In 1962, Věra Čáslavská won her first all-around title at the Czechoslovak Championships, and heading into the World Championships in Prague, the expectations were high for the star of Czechoslovak gymnastics. The Czech-language sports newspaper Stadión printed an article on Čáslavská, which is part profile, part Shakespearean play, and part fairytale.
Note: A fairytale seems bizarre, but pohádky (fairytales) are a vibrant genre in Czech culture. Čáslavská even wrote one about gymnastics in her autobiography, which you can find translated here.
My Thought Bubble: That said, the combination of fairytale and Shakespearean characters is a bit bizarre, but the profile gives us an idea of how Czechoslovak journalists wrote about athletes at the time.

No surprise: The Soviet men’s team defeated the Czechoslovak and East German teams, and Yuri Titov, the 1959 European All-Around Champion, won the all-around title
The surprise: Months before the Prague World Championships, the Czech and East German women defeated the Soviet team, and Čáslavská won the all-around.
Granted, the top Soviet gymnast, Larisa Latynina, was not present. However, Čáslavská’s victory over Astakhova was a harbinger of good things to come. After finishing behind Astakhova at the 1960 Olympics (eighth compared to third) and the 1961 European Championships (tied for third compared to second), Čáslavská finally beat Astakhova during this tri-meet. Then, at the 1962 World Championships, Čáslavská finished second, defeating all the Soviet gymnasts except for Latynina.
Here’s more about the tri-meet, as well as short interviews with several of the Soviet gymnasts. An interesting question came up: Would it be correct to give the judges the optional routines written out before the competition? Not surprisingly, all the athletes said no.
In the lead-up to the 1962 World Championships in Prague, the pages of the Czechoslovak sports periodical Stadión were filled with articles and photos related to gymnastics, one of which told the story behind three gymnasts’ floor routines: Hana Růžičková’s, Věra Čáslavská’s, and Eva Bosáková’s. It’s an interesting article, given that the extant videos do not have sound. Plus, the article contrasts the Czechoslovak style with the Soviet style.
This last point is important because, as we look back on the history of the sport, we tend to group old routines together, categorizing them all as “balletic.” But national teams made a conscientious effort to differentiate their routines and styles.
Another factor to consider: The use of music for individual floor routines was relatively new at the time. 1958 was the first time that music for women’s floor was used at a World Championships or Olympics. As a result, countries were trying to figure out what worked and what didn’t work.

Hana Růžičková didn’t want to be a gymnast. She dreamed of wearing white skating boots, but when those boots never materialized, she started gymnastics in 1956 at the age of fifteen. By 1960, she was a member of the Czechoslovak team that won silver at the Rome Olympics, and one year later, in 1961, Hana Růžičková was the surprise champion of the Czechoslovak Championships. (Věra Čáslavská fell off beam, and Růžičková was able to capitalize on it.)
What follows is a translation of a profile on Růžičková. It was printed in February of 1962, a few weeks after her win at the 1961 Czechoslovak Championships. Not only does it tell the story of a gymnast from a small village who had to balance work, training, and a long commute, but it also raises broader questions, such as: At what age should athletes start special training?
[Note: The age at which Růžičková started gymnastics sometimes varies in articles. For example, the report on the 1961 Championships suggested that she started in 1958.]
